History
Ancient history and settlement.
History of Thailand’s Early Age. The origins of Thailand trace back to prehistoric times with archaeological evidence of early human settlements dating back thousands of years. The region saw the rise of several early civilizations, including the Dvaravati, Srivijaya, and Khmer empires, which significantly influenced its culture, architecture, and religion.
The establishment of the Sukhothai Kingdom in the 13th century marked the beginning of the Thai nation. It was followed by the Ayutthaya Kingdom, which became a major power in Southeast Asia. In the 18th century, the Chakri dynasty founded the Rattanakosin Kingdom, with Bangkok as its capital. Thailand, known historically as Siam, is unique in Southeast Asia for never having been colonized by European powers, allowing it to maintain a rich and continuous cultural heritage that blends indigenous traditions with external influences.

Geography

Geography
Diverse landscapes and natural beauty.
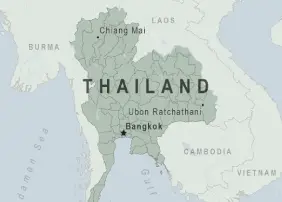
Thailand is located in the heart of Southeast Asia, bordered by Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and Malaysia. It covers an area of approximately 513,120 square kilometres, featuring a diverse landscape that includes mountainous regions in the north, fertile plains in the central area, and stunning beaches along the southern peninsula.
The northern region is known for its forested mountains and ethnic hill tribes, offering cooler climates and natural beauty. Central Thailand is the rice bowl of the country, with extensive paddy fields and the bustling metropolis of Bangkok. The southern region is famed for its tropical islands and beaches, such as Phuket, Koh Samui, and Krabi, which are popular tourist destinations. Thailand’s climate is tropical, characterized by a rainy season, a hot season, and a cool season, supporting a rich biodiversity and vibrant agriculture.
